Netty权威指南读书笔记
Netty权威指南读书笔记
一、I/O基础概念
1、文件描述符
对文件的读写操作会调用内核提供的系统命令,并返回一股file descriptor ,简称fd, 是一个数字,指向内核中的一个结构体(文件路径,数据区等一些属性)。 类似的,对一个socket的读写也会产生相应的描述符(socketfd)。
2、5种I/O模型
UNIX网络编程提供的5种I/O模型:
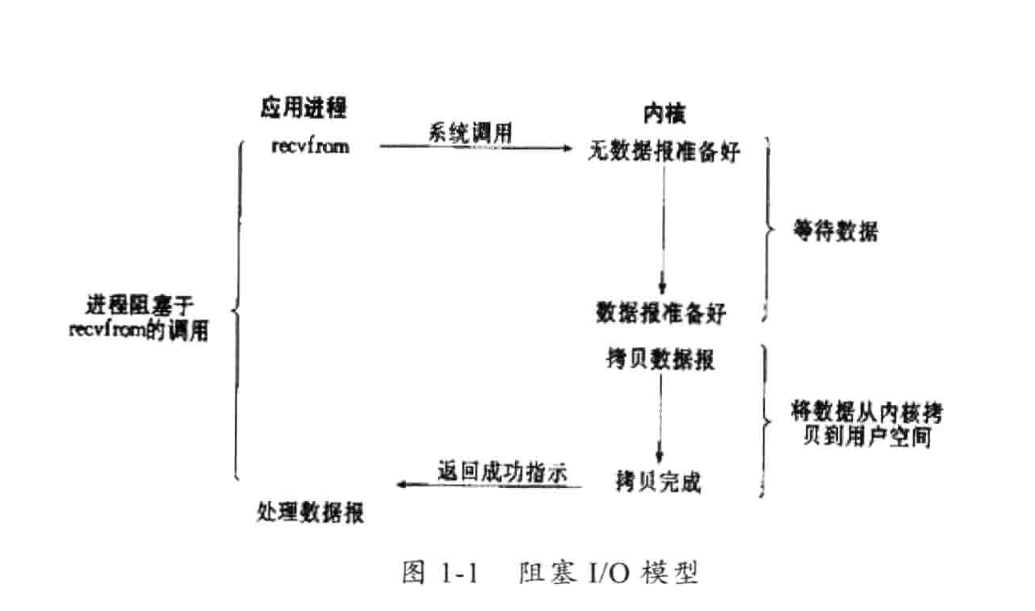
1)阻塞I/O模型:
最常用,默认情况所有文件操作都是阻塞的。
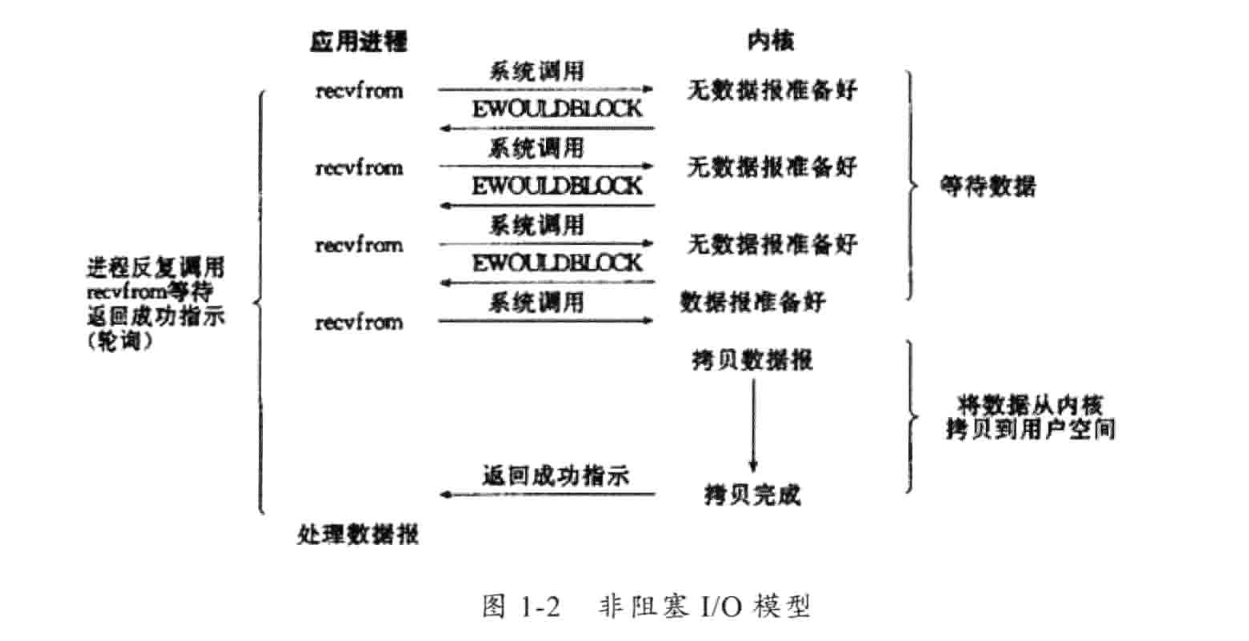
2)非阻塞I/O模型
应用层不断轮询检查内核有无数据到来。
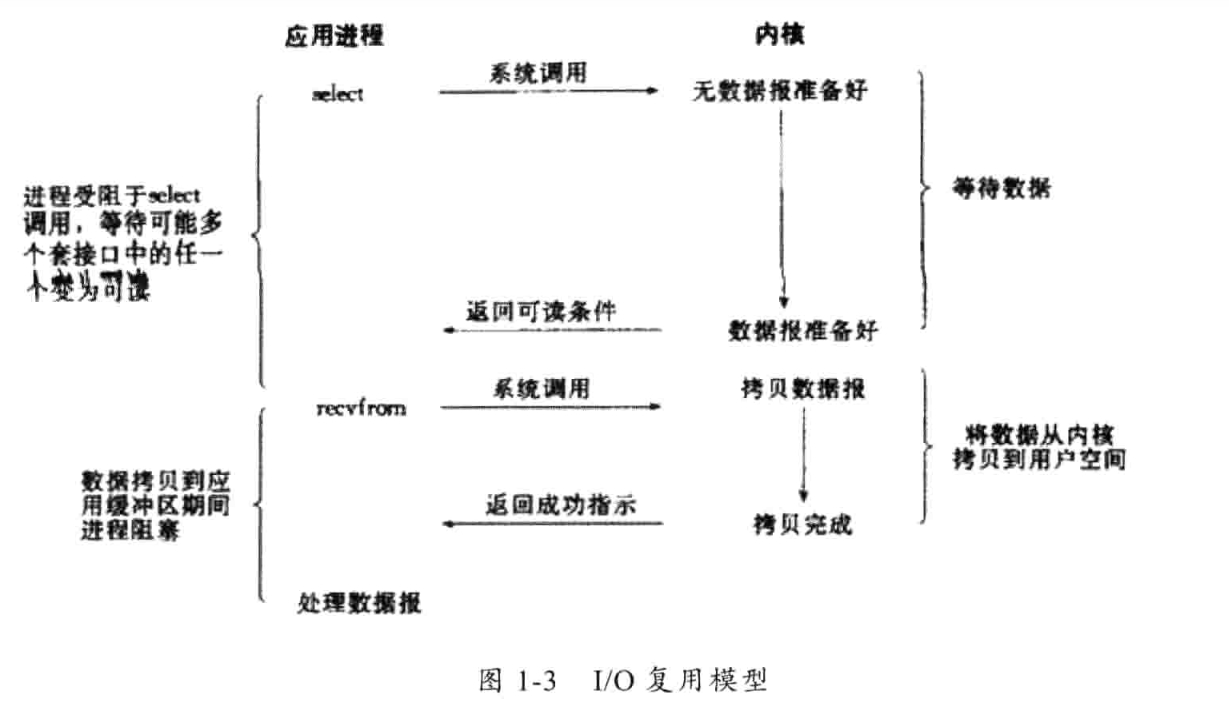
3)I/O复用模型
Linux上提供了select/poll的系统调用,应用进程通过将一个或者多个fd传递给select或者poll,同时阻塞在select上,这样select/poll帮我们监听多个fd是否处于就绪状态。
select/poll通过顺序扫描fd是否就绪,且只支持有限个fd(默认配置是1024个),因此为了克服select的缺点,linux提供了一个epoll的系统调用,epoll的使用基于事件驱动方式代替顺序扫描,性能更高,且对fd没有数量限制,当检测到有fd就绪时,立即回调函数rollback。
这里总结一下epoll和select的区别:
- 支持一个进程打开的socket描述符(fd)数量不受限制(仅受限于操作系统的最大文件句柄数,在1GB内存的机器上大约是10万个句柄左右)
- I/O效率不会随着fd数量的增加而线性下降。(不同于select对全部集合的线性扫描,epoll只会多活跃的fd进行操作)
- 使用mmap加速了内核与用户空间的消息传递(epoll是通过内核和用户空间mmap同一块内存实现,避免了不必要的内存复制)
- epoll的API更加简单
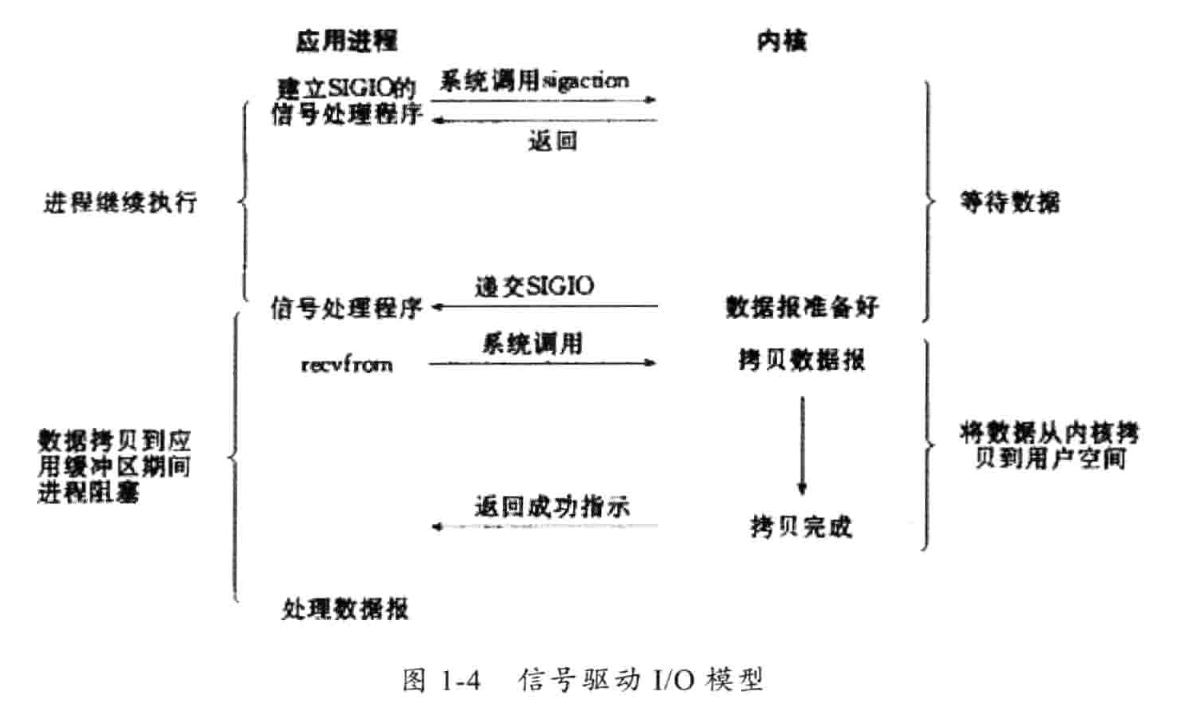
4)信号驱动I/O模型
通过系统调用sigaction执行一个信号处理函数(调用后立即返回进程继续工作,是非阻塞的调用)。当内核数据准备就绪时,就会为该进程生成一个SIGIO信号,通过信号回调通知应用程序调用recvfrom来读取数据,并通知主循环函数处理数据。
5)异步I/O
告知内核启动某个操作,并让内核在整个操作完成后(包括将数据从内核复制到用户自己的缓冲区)通知我们。这种模型与信号驱动模型的主要区别是:信号驱动I/O由内核通知我们何时可以开始一个I/O操作;异步I/O模型由内核通知我们I/O操作何时已经完成。
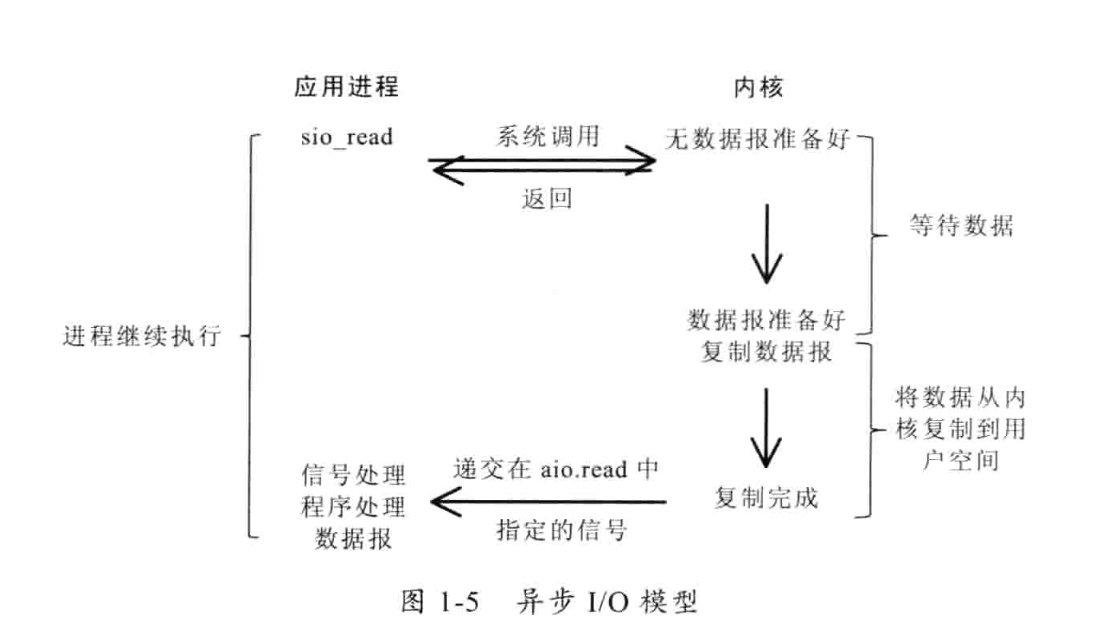
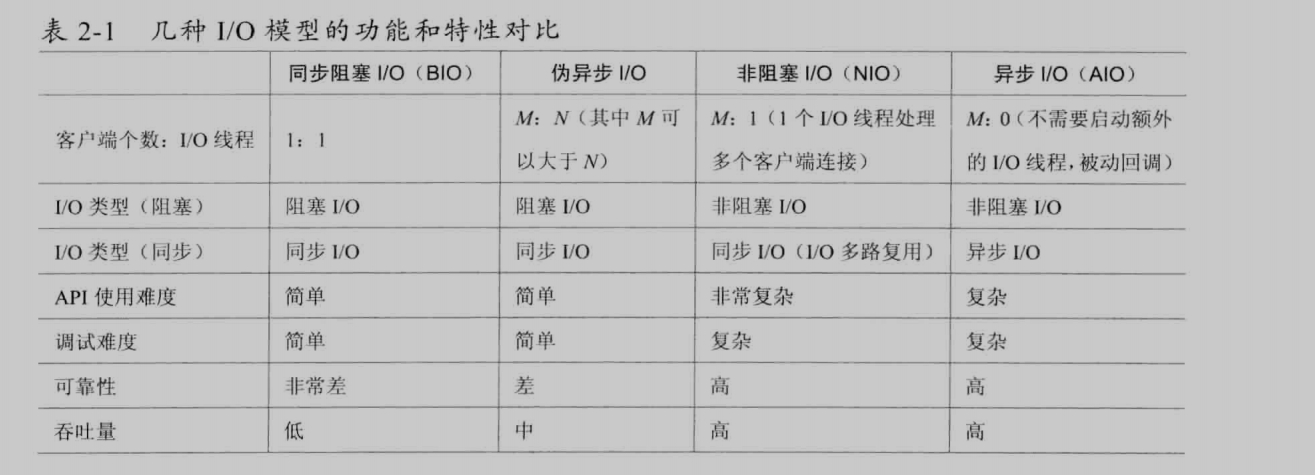
二、NIO编程基本概念
一般低负载、低并发的应用程序可以选择同步阻塞I/O(BIO),而对于高负载、高并发的应用,需要使用NIO的非阻塞模式。
1、缓冲区(Buffer)
在NIO编程中,所有数据都是用Buffer处理的。在读取数据时,它是直接读到缓冲区中;在写入数据时,是写入到缓冲区中。任何时候访问NIO中的数据,都是通过缓冲区进行操作的。
Buffer是NIO类库中的一个对象,包含一些要写入或者要读出的数据。它实际上是一个数组,一般是一个字节数组(ByteBuffer)。它还有其它很多类型,例如针对每一种Java基本类型(除了Boolean)都对应有一种缓冲区,具体如下:
ByteBuffer:字节缓冲区(大多数标准I/O操作都使用它,它除了具有一般缓冲区的操作之外还提供一些特有操作,方便网络读写)
CharBuffer:字符缓冲区
ShortBuffer:短整型缓冲区
IntBuffer:整型缓冲区
LongBuffer:长整形缓冲区
FloatBuffer:浮点型缓冲区
DoubleBuffer:双精度浮点型缓冲区
2、通道(Channel)
Channel就像自来水管一样,网络数据通过Channel读取和写入,Channel和流的不同支出在于它是全双工的,可以同时用于读写操作(而流只是在一个方向流动,必须是InputStream或者OutputStream的子类)。
3、多路复用器(Selector)
4、TCP粘包/拆包
TCP是个“流" 协议,所谓流,就是没有界限的一串数。TCP底层并不了解上层业务数据的具体含义,会根据TCP缓冲区的实际情况进行包的划分,所以一个完整的包可能被TCP拆分成多个包进行发送,也可能把多个小的包封装成一个大的数据包进行发送,这就是TCP粘包和拆包问题。
三、NIO入门应用
1、开发环境搭建
使用maven管理依赖的项目,引入如下依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>io.netty</groupId>
<artifactId>netty-all</artifactId>
<version>5.0.0.Alpha2</version>
</dependency>2、服务端代码
下面简短的业务逻辑代码,即完成了NIO服务端的开发,相比传统基于JDK NIO原生类库的服务端,代码量大大减少,开发难度也降低了很多
package com.gyd.net.netty;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
/**
* @ClassName TimeServer
* @Description 使用netty开发时间服务器的服务端
* @Author guoyading
* @Date 2024/7/1 14:29
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class TimeServer {
public void bind(int port) throws InterruptedException {
//配置服务端的NIO线程组(实际就是Reactor线程组,一个用于接收客户端连接,一个用于进行SocketChannel的网络读写)
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup,workerGroup)
//功能对应JDK NIO类库中的ServerSocketChannel类
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
//配置NioServerSocketChannel的TCP相关参数
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG,1024)
//指定事件的处理类,类似Reactor模式中的handler类,主要用于处理网络IO事件,例如记录日志、对消息进行编解码等
.childHandler(new ChildChannelHandler());
//绑定监听端口,同步等待成功
//调用同步阻塞方法sync(),等待绑定操作完成 。完成之后Netty会返回一个ChannelFuture,它的功能类似于Java的Future,主要用于异步操作的通知回调
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(port).sync();
//调用同步阻塞方法sync(),等待服务端监听端口关闭 。等待服务端链路关闭之后main函数才退出
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
//优雅退出,释放线程池资源
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
private class ChildChannelHandler extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new TimeServerHandler());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
int port = 8080;
new TimeServer().bind(port);
}
}package com.gyd.net.netty;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @ClassName TimeServerHandler
* @Description 对网络事件进行读写操作 通常只需要关注channelRead和exceptionCaught
* @Author guoyading
* @Date 2024/7/1 14:56
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class TimeServerHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
//ByteBuf类似于jdk的ByteBuffer对象,不过它提供了更加强大和灵活的功能
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
byte[] req = new byte[buf.readableBytes()];
buf.readBytes(req);
String body = new String(req, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("Thetime server receive order : "+ body);
String currentTime = "QUERY TIME ORDER".equalsIgnoreCase(body) ? new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()).toString() : "BAD ORDER";
ByteBuf resp = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(currentTime.getBytes());
//异步发送应答消息给客户端
ctx.write(resp);
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
//将消息发送队列中的消息写入到SocketChannel中发送给对方
//从性能角度考虑,为了防止频繁唤醒Selector进行消息发送,Netty的write方法并不直接将消息写入SocketChannel中,调用write方法只是把待发送的消息放到发送缓冲数组中,
//再通过调用flush方法,将发送缓冲区中的消息全部写入到SocketChannel中
ctx.flush();
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
//当发生异常时,关闭ChannelHandlerContext,并释放相关联的句柄等资源
ctx.close();
}
}3、客户端代码
Netty客户端开发比服务端更简单。
package com.gyd.net.netty;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
/**
* @ClassName TimeClient
* @Description TODO
* @Author guoyading
* @Date 2024/7/1 15:30
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class TimeClient {
public void connect(int port, String host) throws InterruptedException {
//配置客户端NIO线程组
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try{
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new TimeClientHandler());
}
});
//发起异步连接操作
ChannelFuture f = b.connect(host,port).sync();
//等待客户端链路关闭
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
//优雅退出,释放NIO线程组
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
int port = 8080;
new TimeClient().connect(port,"127.0.0.1");
}
}package com.gyd.net.netty;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
* @ClassName TimeClientHandler
* @Description TODO
* @Author guoyading
* @Date 2024/7/1 15:41
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class TimeClientHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(TimeClientHandler.class.getName());
private final ByteBuf firstMessage;
public TimeClientHandler(){
byte[] req = "query time order".getBytes();
firstMessage = Unpooled.buffer(req.length);
firstMessage.writeBytes(req);
}
//当客户端和服务端TCP链路建立成功之后,Netty的NIO线程会调用channelActive方法将请求消息发送给服务端
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.writeAndFlush(firstMessage);
}
//当服务端返回应答消息时,channelRead方法被调用
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
byte[] req = new byte[buf.readableBytes()];
buf.readBytes(req);
String body = new String(req,"UTF-8");
System.out.println("Now is : "+ body);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
//释放资源
logger.warning("Unexpectedexception from downstream : "+cause.getMessage());
ctx.close();
}
}4、运行
TimeServer服务端输出:
The time server receive order : query time orderTimeClient客户端输出:
Now is : Mon Jul 01 16:13:43 CST 2024四、TCP粘包/拆包问题
底层TCP无法理解上层的业务数据,所以在底层是无法保证数据包不被拆分和重组的,这个问题只能通过上层应用协议来解决,目前业界主流协议的解决方案归类如下:
1)消息定长,例如每个报文 的大小固定长度200字节,如果不够,使用空位补空格;
2)在包尾增加回车换行符进行分割,例如FTP协议;
3)将消息分为消息头和消息体,消息头中包含表示消息总长度(或者消息体长度)的字段,通常的涉及思路为消息头的第一锅字段使用int32来表示消息的总长度;
4)更复杂的应用层协议。
为了解决TCP粘包/拆包导致的半包读写问题,Netty默认提供了多种编码解码器用于处理半包,这也是其它NIO框架和JDK原生的NIO API无法匹敌的。
1、按行切换解码器
Netty提供很多解决方式,比如LineBasedFrameDecoder+StringDecoder组合就是按行切换的文本解码器,用来解决TCP粘包/拆包问题。
LineBasedFrameDecoder是以换行符为结束标志的解码器。的工作原理是依次遍历ByteBuf中的可读字节,判断看释放有"\n"或者"\r\n",如果有,就以此为结束为止,从可读位置到结束位置区间的字节就组成了一行。如果连续读取到最大长度后仍然没有发现换行符,就会抛出异常,同时忽略掉之前读到的异常码流。
StringDecoder的功能是将接收到的对象转换成字符串,然后继续调用后面的handler。
接下来用代码演示如何使用。
服务端代码:
package com.gyd.net.netty.v2;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @ClassName TimeServerHandler
* @Description 对网络事件进行读写操作 通常只需要关注channelRead和exceptionCaught
* @Author guoyading
* @Date 2024/7/1 14:56
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class TimeServerHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
private int counter;
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
String body = (String) msg;
System.out.println("The time server receive order : "+ body + "; the counter is : " + ++counter);
String currentTime = "QUERY TIME ORDER".equalsIgnoreCase(body) ?
new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()).toString() : "BAD ORDER";
currentTime = currentTime + System.getProperty("line.separator");
ByteBuf resp = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(currentTime.getBytes());
//异步发送应答消息给客户端
ctx.write(resp);
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
//将消息发送队列中的消息写入到SocketChannel中发送给对方
//从性能角度考虑,为了防止频繁唤醒Selector进行消息发送,Netty的write方法并不直接将消息写入SocketChannel中,调用write方法只是把待发送的消息放到发送缓冲数组中,
//再通过调用flush方法,将发送缓冲区中的消息全部写入到SocketChannel中
ctx.flush();
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
//当发生异常时,关闭ChannelHandlerContext,并释放相关联的句柄等资源
ctx.close();
}
}package com.gyd.net.netty.v2;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.LineBasedFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
/**
* @ClassName TimeServer
* @Description 使用netty开发时间服务器的服务端
* @Author guoyading
* @Date 2024/7/1 14:29
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class TimeServer {
public void bind(int port) throws InterruptedException {
//配置服务端的NIO线程组(实际就是Reactor线程组,一个用于接收客户端连接,一个用于进行SocketChannel的网络读写)
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup,workerGroup)
//功能对应JDK NIO类库中的ServerSocketChannel类
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
//配置NioServerSocketChannel的TCP相关参数
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG,1024)
//指定事件的处理类,类似Reactor模式中的handler类,主要用于处理网络IO事件,例如记录日志、对消息进行编解码等
.childHandler(new ChildChannelHandler());
//绑定监听端口,同步等待成功
//调用同步阻塞方法sync(),等待绑定操作完成 。完成之后Netty会返回一个ChannelFuture,它的功能类似于Java的Future,主要用于异步操作的通知回调
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(port).sync();
//调用同步阻塞方法sync(),等待服务端监听端口关闭 。等待服务端链路关闭之后main函数才退出
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
//优雅退出,释放线程池资源
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
private class ChildChannelHandler extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new TimeServerHandler());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
int port = 8080;
new TimeServer().bind(port);
}
}客户端代码:
package com.gyd.net.netty.v2;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
* @ClassName TimeClientHandler
* @Description TODO
* @Author guoyading
* @Date 2024/7/1 15:41
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class TimeClientHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(TimeClientHandler.class.getName());
private int counter;
private byte[] req;
public TimeClientHandler(){
req = ("query time order" + System.getProperty("line.separator")).getBytes();
}
//当客户端和服务端TCP链路建立成功之后,Netty的NIO线程会调用channelActive方法将请求消息发送给服务端
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ByteBuf message = null;
//模拟连续向服务端发送1W个消息
for (int i=0;i<10000;i++) {
message = Unpooled.buffer(req.length);
message.writeBytes(req);
ctx.writeAndFlush(message);
}
}
//当服务端返回应答消息时,channelRead方法被调用
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
String body = (String)msg;
System.out.println("Now is :"+ body + " ; the counter is : " + ++counter);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
//释放资源
logger.warning("Unexpected exception from downstream : "+cause.getMessage());
ctx.close();
}
}package com.gyd.net.netty.v2;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.LineBasedFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
/**
* @ClassName TimeClient
* @Description TODO
* @Author guoyading
* @Date 2024/7/1 15:30
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class TimeClient {
public void connect(int port, String host) throws InterruptedException {
//配置客户端NIO线程组
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try{
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new TimeClientHandler());
}
});
//发起异步连接操作
ChannelFuture f = b.connect(host,port).sync();
//等待客户端链路关闭
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
//优雅退出,释放NIO线程组
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
int port = 8080;
new TimeClient().connect(port,"127.0.0.1");
}
}2、按分隔符切换解码器
1)DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder
以分隔符做结束标志的消息解码器
2)FixedLengthFrameDecoder
定长消息解码器,无论一次接收到多少数据报,它都会按照设置的固定长度进行解码,如果是半包消息,则会缓存半包消息并等待下个包到达后进行拼包,直到读取到一个完整的包.
有了上述两个解码器,再结合其它的解码器,如字符串解码器等,可以轻松地完成对很多消息的自动解码,而且不需要考虑TCP粘包/拆包导致的读半包问题。上述两个解码器的使用也很简单,只需要将其添加到对应ChannelPipeline的起始位置即可。
代码示例:
服务端:
package com.gyd.net.netty.echo;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.FixedLengthFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
/**
* @ClassName EchoServer
* @Description TODO
* @Author guoyading
* @Date 2024/7/2 14:02
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class EchoServer {
public void bind(int port) throws InterruptedException {
//配置服务端的NIO线程组
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup,workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG,100)
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
//使用"$_"作为分隔符
ByteBuf delimiter = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("$_".getBytes());
//固定长度解码器,按固定20字节截取的解码器
// ch.pipeline().addLast(new FixedLengthFrameDecoder(20));
//1024表示单条消息的最大长度,当达到该长度后仍然没有查到分隔符,就抛出TooLongFrameException异常,防止由于异常码流缺失分隔符导致的内存溢出,这是Netty解码器的可靠性保护。
ch.pipeline().addLast(new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(1024,delimiter));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new EchoServerHandler());
}
});
//绑定端口,同步等待成功
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(port).sync();
//等待服务端监听端口关闭
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
// 优雅退出,释放线程池资源
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
int port = 8080;
new EchoServer().bind(port);
}
}package com.gyd.net.netty.echo;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
/**
* @ClassName EchoServerHandler
* @Description TODO
* @Author guoyading
* @Date 2024/7/2 13:50
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class EchoServerHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
int counter = 0;
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
//由于DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder自动对请求消息进行了解码,后续的ChannelHandler接收到的msg对象就是个完整的消息包了。
//第二个ChannelHandler是StringDecoder,将ByteBuf解码成字符串对象
//第三个EchoServerHandler接收到的msg消息就是解码后的字符串对象。
String body = (String) msg;
System.out.println("This is " + ++counter + " times receive client : [" + body+"]");
body += "$_";
ByteBuf echo = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(body.getBytes());
ctx.writeAndFlush(echo);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();// 发生异常,关闭链路
}
}客户端:
package com.gyd.net.netty.echo;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.FixedLengthFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
/**
* @ClassName EchoClient
* @Description TODO
* @Author guoyading
* @Date 2024/7/2 15:48
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class EchoClient {
public void connect(int port, String host) throws InterruptedException {
//配置客户端NIO线程组
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>(){
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ByteBuf delimiter = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("$_".getBytes());
//固定长度解码器,按固定20字节截取的解码器
// ch.pipeline().addLast(new FixedLengthFrameDecoder(5));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(1024,delimiter));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new EchoClientHandler());
}
});
//发起异步连接操作
ChannelFuture f = b.connect(host,port).sync();
//等待客户端链路关闭
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
//优雅退出,释放NIO线程组
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
int port = 8080;
new EchoClient().connect(port,"127.0.0.1");
}
}package com.gyd.net.netty.echo;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
/**
* @ClassName EchoClientHandler
* @Description TODO
* @Author guoyading
* @Date 2024/7/2 15:53
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class EchoClientHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
private int counter;
static final String ECHO_REQ = "Hi,server! Welcome to Netty.$_";
public EchoClientHandler(){}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
//在TCP链路建立成功之后循环发送请求消息给服务端
for (int i=0;i<10;i++) {
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(ECHO_REQ.getBytes()));
}
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
//打印服务端应答消息同时进行计数
System.out.println("This is " + (++counter) + " times receive server : [ " + msg + "]");
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.flush();
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}五、序列化技术(编解码)
1、JAVA序列化
JAVA序列化技术在JDK1.1版本就已经提供,只需要对象实现java.io.Serializable并生成序列ID即可,但是它存在很多问题,因此在远程服务调用(RPC)中很少用Java序列化技术进行消息的编解码和传输。缺点如下:
无法跨语言
Java序列化技术使用的是Java语言内部协议,其它语言不支持,对于Java序列化后的字节数组,其它语言无法反序列化。
序列化后的码流太大
针对如下的pojo对象:
public class UserInfo implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private String userName; private int userID; }Java序列化技术序列化的字节数组大小是ByteBuffer通用二进制编码技术的5倍左右。
序列化性能差
针对UserInfo这个POJO编码100万次,Java序列化技术耗时大约是7s,而二进制编码技术只需要不到1秒,Java序列化的性能只有二进制编码的6.17%左右。
下面是示例代码。
服务端:
package com.gyd.net.netty.serializable.jdk;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.serialization.ClassResolvers;
import io.netty.handler.codec.serialization.ObjectDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.serialization.ObjectEncoder;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
/**
* @ClassName SubReqServer
* @Description 订购服务端
* @Author guoyading
* @Date 2024/7/3 10:21
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class SubReqServer {
public void bind(int port) throws InterruptedException {
//配置服务端的NIO线程组
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup,workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG,100)
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
//ObjectDecoder负责对实现了Serializable的POJO对象进行解码(使用weakCachingConcurrentResolver创建线程安全的WeakReferenceMap对类加载器进行缓存,支持多线程并发访问)
//同时为了防止异常码流和解码错位导致的内存溢出,这里将单个对象最大序列化后的字节数组长度设置为1M,作为demo完全够了
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ObjectDecoder(1024*1024, ClassResolvers.weakCachingConcurrentResolver(this.getClass().getClassLoader())));
//ObjectEncoder负责对实现了Serializable的POJO对象进行编码
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ObjectEncoder());
//SubReqServerHandler负责对客户端请求进行具体业务逻辑处理
ch.pipeline().addLast(new SubReqServerHandler());
}
});
//绑定端口,同步等待成功
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(port).sync();
//等待服务端监听端口关闭
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
//优雅退出,释放线程池资源
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
int port = 8080;
new SubReqServer().bind(port);
}
}package com.gyd.net.netty.serializable.jdk;
import com.gyd.net.netty.serializable.SubscribeReq;
import com.gyd.net.netty.serializable.SubscribeResp;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
/**
* @ClassName SubReqServerHandler
* @Description 服务端业务逻辑处理
* @Author guoyading
* @Date 2024/7/3 10:32
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class SubReqServerHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
//由于ObjectDecoder已经帮我们把字节数据自动解码成了SubscribeReq对象,这里直接强转即可。
SubscribeReq req = (SubscribeReq) msg;
if ("guoyading".equalsIgnoreCase(req.getUserName())){
System.out.println("Service accept client subscribe req : [" + req.toString() + "]");
ctx.writeAndFlush(resp(req.getSubReqID()));
}
}
private SubscribeResp resp(int subReqID) {
SubscribeResp resp = new SubscribeResp();
resp.setSubReqID(subReqID);
resp.setRespCode(0);
resp.setDesc("Netty book order succeed, 3days later, sent to the designated address");
return resp;
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();//发生异常,关闭链路
}
}客户端:
package com.gyd.net.netty.serializable.jdk;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.serialization.ClassResolvers;
import io.netty.handler.codec.serialization.ObjectDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.serialization.ObjectEncoder;
/**
* @ClassName SubReqClient
* @Description 订购客户端
* @Author guoyading
* @Date 2024/7/3 11:25
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class SubReqClient {
public void connect(int port,String host) throws InterruptedException {
//配置客户端NIO线程组
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY,true)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ObjectDecoder(1024, ClassResolvers.cacheDisabled(this.getClass().getClassLoader())));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ObjectEncoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new SubReqClientHandler());
}
});
//发起异步连接操作
ChannelFuture f = b.connect(host,port).sync();
//等待客户端链路关闭
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
//优雅退出,释放NIO线程组
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
int port = 8080;
new SubReqClient().connect(port,"127.0.0.1");
}
}package com.gyd.net.netty.serializable.jdk;
import com.gyd.net.netty.serializable.SubscribeReq;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
/**
* @ClassName SubReqClientHandler
* @Description TODO
* @Author guoyading
* @Date 2024/7/3 14:21
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class SubReqClientHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
public SubReqClientHandler(){}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
//在链路激活时,连续发送10条订购消息
for (int i=0;i<10;i++){
ctx.write(subReq(i));
}
ctx.flush();
}
private SubscribeReq subReq(int i) {
SubscribeReq req = new SubscribeReq();
req.setAddress("xxxx上海大学");
req.setPhoneNumber("133xxxxxx");
req.setProductName("redis入门教程");
req.setSubReqID(i);
req.setUserName("guoyading");
return req;
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Received server response : ["+ msg + "]");
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.flush();
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}2、业界主流序列化框架
1)Protobuf
Protobuf全称:Google Protocol Buffers。
Protobuf是由谷歌开源,它将数据结构以.proto文件进行描述,通过代码生成工具可以生成对应数据结构的POJO对象和Protobuf相关的方法和属性。
它的特点总结如下:
- 结构化数据存储格式(XML、JSON等);
- 高效的编解码性能;
- 语言无关、平台无关、扩展性好;
- 官方支持Java、C++和Python这三种语言
- 自动代码生成
2)Thrift
Thrift是Facebook开源的项目,产生的初衷是为了解决Facebook各系统间大数据量的传输通信以及系统之间语言环境不同需要跨平台的特性。
它支持多种程序语言,如C++、C#、Cocoa、Erlang、Haskell、Java、Ocami、Perl、PHP、Python、Ruby、Smalltalk;
3)JBoss Marshalling
JBoss Marshalling是一个Java对象序列化API包,解决了JDK自带序列化包的很多问题,但是又保持跟java.io.Serializable接口的兼容,同时增加了一些可调的参数和附加特性,并且这些参数和特性可以通过工厂类进行配置。
相比Protobuf和Thrift,JBoss Marshalling更多是在JBoss内部使用,目前在业界应用范围比较小。